
Did You Know?
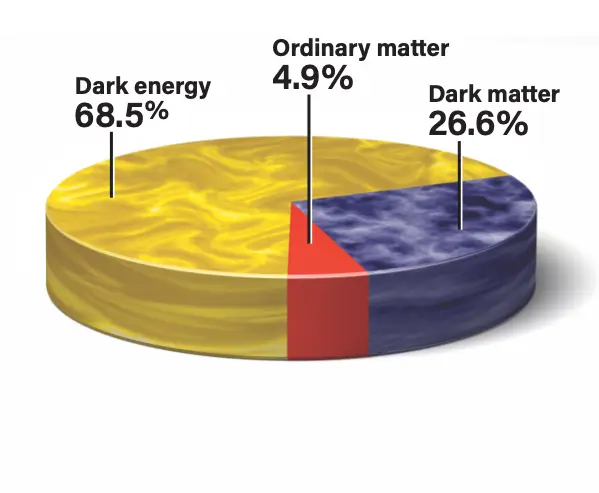
Do you realize that the universe contains approximately 27% dark matter and 5% normal matter, yet no one has ever observed dark matter? Scientists throughout the world have been studying the universe since the beginning of time, but the mystery of dark matter remains a secret.
What Is Dark Matter?
Dark matter could be seen as a type of matter made up of particles that scientists cannot observe using telescopes. Scientists do, however, understand the effects of dark matter by studying the physical behavior of everything it influences. As galaxies spin rapidly, stars should fly off into space. However, gravity holds them together, and an unseen force pulls on them. Astronomers refer to this hidden mass as dark matter. Dark matter emits no light, reflects no light, and does not absorb light. Because scientists cannot detect light from dark matter, observation becomes extremely difficult.
How Did Astronomers Discover the Existence of Dark Matter?
Astronomers measure how quickly stars orbit the centers of galaxies by observing galactic motion. When they study star movement, they discover stars move far too fast for normal matter to explain. Additionally, astronomers observe gravitational lensing, where light bends around invisible masses.
Cosmic background radiation also reflects the influence of dark matter on galaxies. NASA states that dark matter weighs five times more than all visible matter combined.

Why Dark Matter Is Hard to Detect
Dark matter does not interact with light or energy like normal matter. Because of this, scientists cannot detect it using physical methods. As a result, researchers built laboratories deep underground to reduce noise from cosmic rays. These controlled environments help scientists search for weak signals.
So far, experiments have not revealed a signal clearly identified as dark matter. Additionally, billions of dark matter particles may pass through Earth every second, yet no laboratory has detected one.
Technology Limits
Scientific experiments require precise tools. For dark matter research, scientists need sensors that detect extremely small energy changes. Dark matter produces almost no energy fluctuations.
Therefore, scientists must push technology to its limits. For example, detectors must identify one dark matter particle among trillions of ordinary particles. Currently, no detector can achieve this accuracy. As technology advances, scientists continue upgrading their equipment to improve results.
Confusion Caused by Different Theories
Scientists do not agree on what dark matter is. Some believe it consists of weakly interacting particles. Others suggest axions. Some scientists question dark matter’s existence and propose modified gravity instead.
Because theories differ, researchers design experiments to detect different signals. As a result, no single experiment tests all theories at once. This disagreement slows the discovery process.
The Expected Science of Psychology
Expectations influence human behavior, including scientific research. Scientists expect dark matter to behave in certain ways. Consequently, they design experiments to match those expectations. When results fail, frustration increases. Psychology shows people resist abandoning familiar beliefs. Therefore, researchers often continue supporting widely accepted theories.
Eventually, new ideas gain acceptance. However, this process takes time.

The Fear of Being Wrong
Scientists, like everyone else, fear failure. Publishing incorrect results can damage careers. Because of this, researchers act cautiously and demand strong verification before announcing discoveries. This caution protects scientific integrity, but it can slow major breakthroughs.
Read more: Explore The Multiverse Of Your Mind
The Mysterious Nature of Dark Matter and Human Curiosity
Humans feel drawn to mystery. This curiosity drives exploration. At the same time, uncertainty causes discomfort. Psychologists call this “intolerance of uncertainty.” As a result, scientists work harder to find answers. Dark matter creates both motivation and challenge.
Read more: Quantum Reality and Our Consciousness
Statistics Explain the Challenge
More than 100 experiments worldwide search for dark matter. None have confirmed direct detection. The Large Hadron Collider also searched for indirect evidence. Results remain unclear. Despite this, funding continues because strong theoretical support exists.
The Use of Space Telescopes
Space missions help scientists indirectly. Satellites map galaxy clusters to show dark matter distribution. The Planck satellite refined dark matter estimates. However, space telescopes cannot directly observe dark matter particles. They reveal effects, not the particles themselves.
The Future
New detectors will launch soon. Technology improves every year. Artificial intelligence now assists data analysis. International cooperation also increases success chances. Eventually, clear data may appear. Until then, patience remains essential.
Thoughts Towards the End
Dark matter likely exists, but scientists lack direct proof. Science moves slowly and carefully. Human psychology affects discovery speed. Fear, belief, and curiosity all play roles. Still, researchers continue searching. One day, dark matter may reveal itself. Until then, the universe keeps its secrets.



Leave a Reply