
Did You Know?
Did you know that adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night for a healthy brain? Unfortunately, research reveals that more than 35% of adults get less than seven hours of sleep per night. Even more alarming, close to 1 in 5 people experience chronic sleep deprivation. As a result, the silent suffering of brain health occurs worldwide.
Sleep appears to be easy. However, sleep affects every aspect of brain function. When sleep is neglected, the brain suffers changes.
What Is Sleep Deprivation?
Sleep deprivation occurs when individuals fail to get sufficient sleep. This issue may occur for one night or for several years. Sometimes, work hours contribute to this issue. Other times, stress, anxiety, or habits are the cause. Often, individuals deliberately neglect sleep.

Why Sleep is Important for the Brain
Sleep provides the brain with time to heal itself. During sleep, brain cells heal. In addition, memory centers process information. At the same time, emotional regulation rebalances itself.
If the brain does not get enough sleep, these functions do not occur effectively. Consequently, the brain has trouble functioning the next day. As a result, sleep functions as fuel for the brain.
What Occurs in the Brain When It Does Not Get Enough Sleep
If the amount of sleep reduces, the messages in the brain slow down. Brain cells do not communicate effectively. As a result, thinking becomes foggy. In addition, the ability to focus decreases. Reaction times slow down. As a result, errors occur frequently.
In addition, judgment deteriorates. The brain becomes less accurate. With time, this continues to deteriorate. With time, the brain suffers the consequences. Slowly, performance declines. Later, damage becomes visible.
Memory Problems Show Up Quickly
Sleep is important for storing memories in the brain. Without sleep, the brain cannot store memories. New information is quickly forgotten. Old memories are also weakened. Studies show that people who do not sleep can remember as much as 40% less information. Thus, learning becomes more difficult. Students experience this problem badly. Also, workers experience it.
Emotional Control Falls Apart
Sleep deprivation impacts emotions badly. The emotional part of the brain takes over. The amygdala is highly active. This part of the brain controls fear and anger. However, the rational part of the brain is weakened. As a result, emotional responses are increased. Thus, small issues become huge. It is difficult to think clearly.
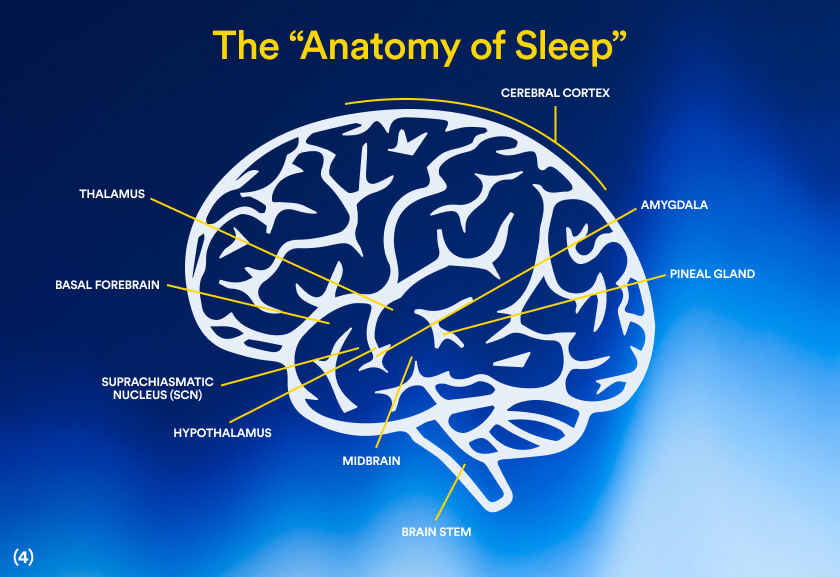
Psychology Behind Mood Changes
From a psychological perspective, sleep controls mood. Without sleep, mood control is lost. People get angry easily. Patience is reduced dramatically. In addition, feelings of sadness increase. Anxiety builds up quickly. Studies show that poor sleep doubles the risk of depression. As a result, sleep is the first thing that therapists treat.
Sleep Deprivation and Anxiety
Sleep deprivation increases anxiety. The brain remains in alert mode. Stress hormones increase. Relaxation becomes difficult. As a result, the brain anticipates danger everywhere. Thoughts spiral easily. Psychologists associate chronic sleep deprivation with panic disorders. Thus, sleep promotes emotional security.
Loss of Focus and Attention
Sleep deprivation affects attention. Also, the brain lacks focus quickly. When working, the brain wanders. Everything becomes more difficult. Concurrently, multitasking completely fails. Research indicates staying awake for 18 hours impairs focus like alcohol intoxication. Thus, sleep preserves focus.
Decision-Making Becomes Risky
The brain processes decisions during sleep. Without sleep, this function deteriorates. Individuals pursue short-term gains. Long-term consequences become insignificant. As a result, impulsive decisions become common. Research indicates that sleep deprivation leads to increased gambling and risk-taking. Consequently, judgment becomes impaired.
Human Behavior Changes Due to Sleep Loss
Sleep loss affects social behavior. Humans behave in different ways. Empathy declines. There are more misunderstandings. Moreover, communication deteriorates. Tone turns aggressive. Psychologists explain that sleep loss leads to a lack of trust and cooperation. Consequently, relationships deteriorate.
Sleep and Stress Hormones
Sleep regulates cortisol levels. Cortisol is responsible for stress regulation. However, sleep loss leads to an increase in cortisol levels. Stress remains active throughout the day. Excessive cortisol damages memory cells. It also damages the immune system. Consequently, sleep is essential for the protection of both the brain and the body.
Long-Term Brain Damage
Chronic sleep loss causes permanent brain damage. Brain cells reduce in size over time. Brain connections become weak. Finally, cognitive function slows down permanently. Studies show that chronic sleep loss increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Protein buildup accelerates in the absence of sleep. Consequently, sleep is essential for the long-term protection of the brain.
The Brain’s Cleaning System Fails to Function
The brain cleanses itself during deep sleep. The brain eliminates toxic waste. This process occurs mostly at night. However, sleep loss causes the brain to retain toxic waste. Scientists explain that the failure of this process causes the brain to age. Consequently, sleep delays brain aging.
Sleep Deprivation and Mental Health Disorders
Sleep deprivation exacerbates mental health issues. Symptoms worsen. Anxiety disorders become more powerful. Depression becomes more severe. Additionally, bipolar mood changes worsen. Mental health professionals focus on improving sleep. Sleep regulates emotions.
Read more: Social Media & Science of Human Interaction
Children and Teen Brain Development
Teen brains require more sleep. Development requires sleep. Unfortunately, many teens sleep fewer than 6 hours. This negatively affects learning and emotional control. Research indicates that sleep-deprived teens have poor academic performance. Mood changes worsen dramatically.

Sleep Deprivation in the Workplace
Sleep deprivation negatively affects work performance. Productivity declines. Errors increase. Creativity declines. In hazardous occupations, accidents increase. Research indicates sleep deprivation is responsible for 20% of workplace accidents. Thus, sleep saves lives.
Society and Sleep Deprivation
Modern society promotes sleep deprivation. Work-related stress increases. Technology contributes to poor habits. Electronic devices delay sleep. Social media robs sleep time. Thus, society needs to appreciate sleep more. Healthy brains require a change in society.
Easy Methods to Preserve Brain Health
Healthy practices enhance sleep quality. First, maintain regular sleep schedules. Second, avoid screens before bedtime. Third, cut back on caffeine consumption. In addition, establish a relaxing sleep environment.
Read more:How Childhood Shapes Adult Behavior
The Role of Psychology in Sleep Practices
Psychology affects sleep behavior. Beliefs drive practices. Most individuals romanticize sleep deprivation. This attitude damages health. Fear of missing out leads to delayed sleep. Psychologists promote a change in sleep beliefs. Healthy thinking promotes improved sleep.
Conclusion
Sleep deprivation alters the brain in profound ways. Memory declines rapidly. Emotions become imbalanced. Decision-making fails. Psychology reveals that behavioral changes occur due to sleep deprivation. Science verifies the long-term harm. Sleep is not an option. The brain requires it every day. Preserving sleep preserves life.



Leave a Reply